Want to squeeze maximum effectiveness from your sales funnel and make your acquired customers purchase as many products as possible? You can do it with a popular strategy of cross-selling.

The cross-selling technique is every step of the way in eCommerce. With or without realizing it, all of us meet this strategy. Brands “convince” us to buy supplementary products when buying the core product.
Promoting many add-on products when customers make a purchase is a cross-sell strategy. It works with proven results. So, if you don’t implement it in your eCommerce strategy yet, it’s high time to do that.
Let’s figure out below what cross-selling is and discuss some of the best cross-selling examples to get you more profound insight.
What is cross-selling?
Cross-selling technique implies that when a consumer makes a purchase, the algorithm suggests that they buy another product, which is supplementary or ancillary to the original purchase. For example, customers order a smartphone online. Then, a small window next to check out suggests they buy a case for the chosen model.
You likely experienced cross-selling yourself when making online purchases. Most online stores have sections “customers also like”, “you might also be interested”, and similar sections, which are the most popular cross-sell strategies.
While it’s accepted that cross-selling technique is primarily applicable for online commerce, offline businesses can also successfully utilize it. For example, when a waiter suggests you order a glass of wine which “goes perfectly” with your ordered pizza, that’s also an example of cross-selling.
Cross-selling is not the same as Upselling and Downselling
The idea of trying to sell a similar product to an already purchased one is also applicable for upselling and downselling. However, there are fundamental differences between those two techniques and cross-selling.
In the case of cross-selling, you suggest products compatible with the one that the client has already bought. However, in case of upselling or downselling, you offer the same product in a higher or lower pricing niche.
For example, if a customer chooses a middle-size bag of the X brand, and the algorithm also starts showing him the bigger size of the same bag, this is upselling. It relies on assumptions of customer payability.
Downselling is the opposite of upselling. In this case, stores suggest the same products of lower price niche to the customers. Downselling is used not to lose customers with a limited budget.
Is cross-selling beneficial for the business?
Cross-sell strategies help a good number of companies worldwide increase revenue. Meanwhile, it costs close to zero to implement this auto-suggestion strategy, especially when compared to marketing campaigns that companies would invest in otherwise to increase sales.
Cross-selling technique increases the earning per customer and customer lifetime value.
Besides, cross-selling also improves customer experience, as many buyers find it convenient to have relevant suggestions for their made purchases. However, the key thing here is making relevant suggestions to buyers beyond just promoting company products.
If an appropriate data-based process is working behind cross-selling, businesses can generate unique packaged selling products for every buyer. Cross-selling will not generate significant results and can even annoy buyers in the opposite case.
To sum up, if a cross-selling technique focuses on generating more value for the customers, it would also increase company revenues.
To make this idea more straightforward for you, let’s discuss below some of the cross-selling best practices and examples.
Cross-selling examples in retail
Adidas
Are you a fan of sports clothing? If you are and have ever shopped on the official website of Adidas, you must probably face the picture below.

Once a user chooses a specific sneaker, the algorithm suggests a total look from Adidas that matches the bought shoes.
ASOS
A famous British fashion brand, ASOS is another cross-selling example that successfully utilizes the “shop the look” system. Similar to Adidas, this helps customers see what other items might go on with their purchased item to form a total look.
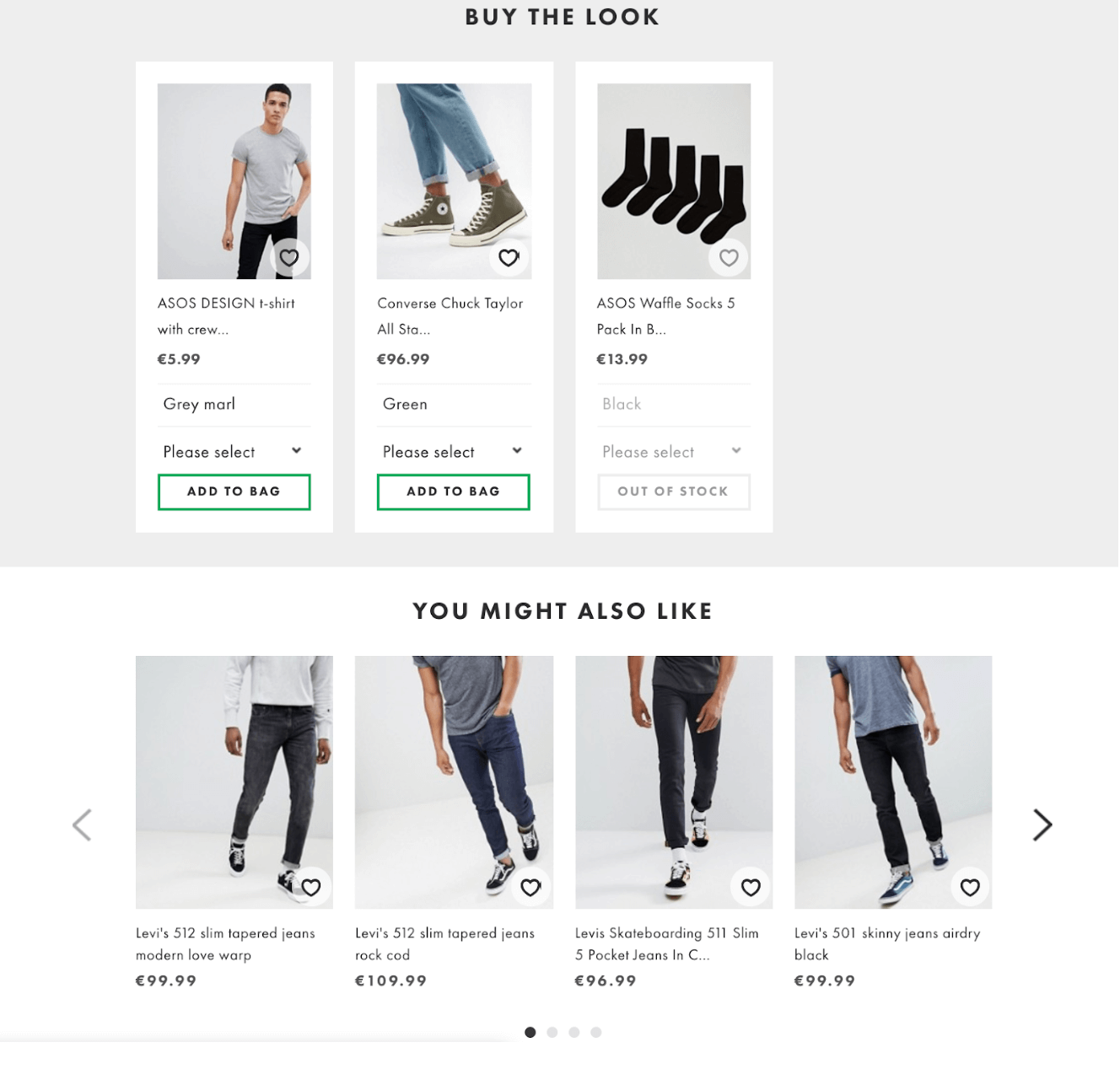
The ASOS’s cross-selling technique is unique, as it often suggests items even before the customer adds something to the shopping bag or makes a purchase.
Cross-selling examples of offering bundles
One of the cross-selling best practices is offering customers to buy products in a bundle. The bundle should be at a more affordable price than purchasing each item separately. This cross-selling technique usually works well in the case of supplementary products. Those are products customers have to buy if they want to utilize their initially bought item properly.
DigitalRev
To illustrate what was said above, let’s take a look at how DigitalRev offers to buy Canon with all its necessary tech supplies at a particular package.
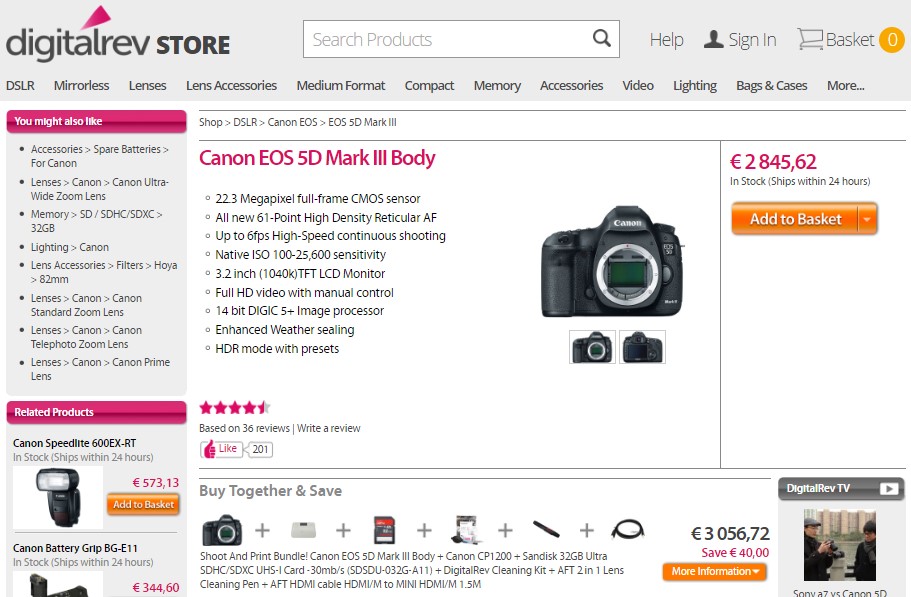
In the case of Adidas, customers might skip buying T-shirts when they buy shoes. That’s because those two products can be used completely independently. However, in the case of the Canon EOS 5D Mark III Body illustrated above, customers are more likely to use the offered cross-sell opportunity.
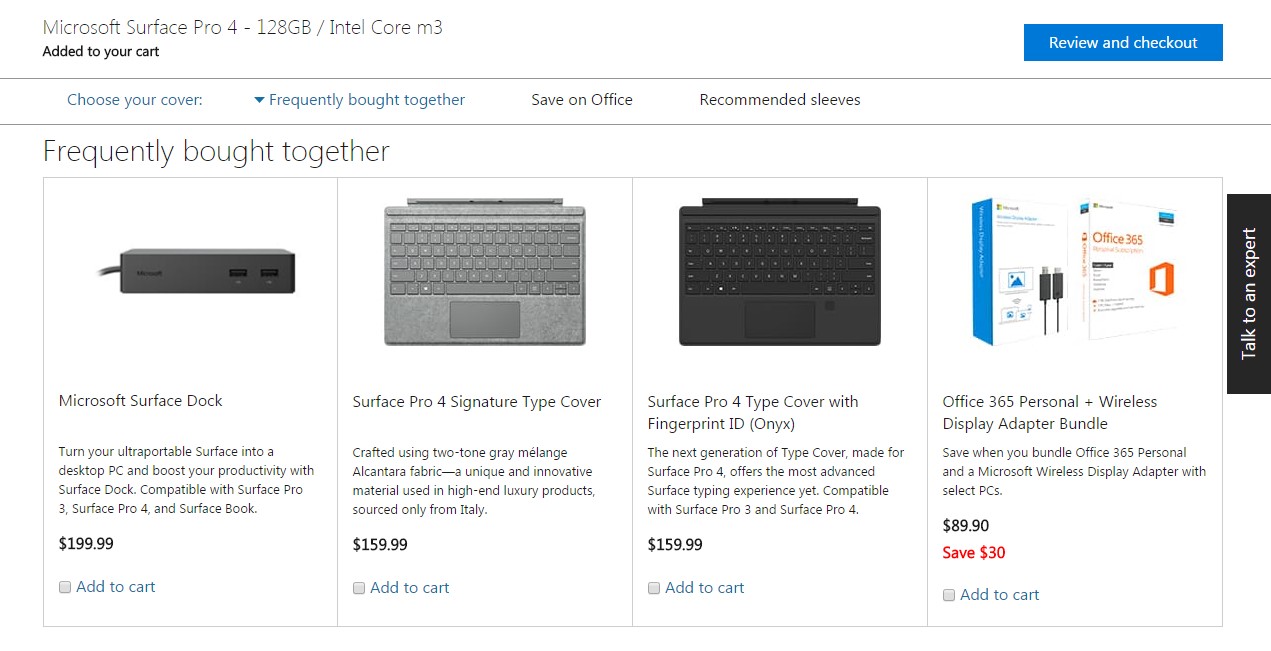
Microsoft
Here is also a similar bundle from Microsoft. The bundles are formed based on the logic that if many customers usually buy all those items together, this is likely to tempt other new customers.
Cross-selling examples of offering bonus products
Many companies offer bundles, where customers receive some item(s) for free if buying certain products in combination. The same cross-sell strategy can work well if some of the products within a bundle have a discount.
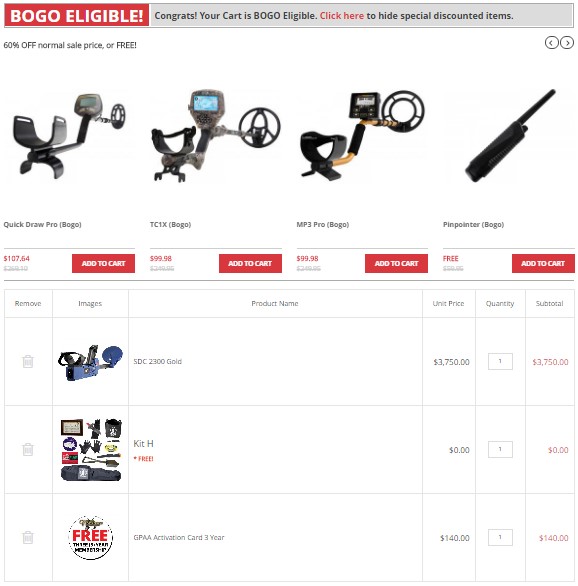
Metal Detector
Just in case you haven’t met such type of cross-selling strategy, here is how Metal Detector do it. Customers have special eligibility factors, and they are notified that by buying certain items, they will become eligible for acquiring some product for free.
Wrap up
We hope the above cross-selling examples gave you a thorough insight into utilizing the technique to increase revenues. Once you start implementing the system, it’s necessary to properly monitor results to understand which types of suggestions work well.
For not tracking this data manually, we suggest you use automated inventory management software, which will give you real-time updates on sales, revenues, and each separate item’s performance.







