If you have heard about retail, wholesale, the prices then you probably would like to know the differences. That is why we are going to analyze the main aspects of wholesale and retail so that we can understand the difference between retail price VS wholesale price.

Wholesale Price and Retail Price Definition
What is retail and wholesale?
Due to modern supply chain technologies, business holders have the choice of different delivery systems. Wholesale and retail are the two effective methods of business that are based on products. They are popular distribution methods – the main components of the supply chain. When the manufacturers make the products in large amounts, they are also supposed to be sold in those amounts. The wholesalershttps://blog.dsmtool.com/dropshipping-suppliers/best-wholesale-suppliers/ are hence for this process (to buy things in bulks). After the next “player” comes – the retailer, who buys stuff from the wholesaler and sells to the final buyers in smaller amounts (piece by piece).
Thus, wholesale deals with a large number of products, that’s to say it is bulk selling, retail works with selling smaller amounts of products. The absence of both the whole supply chain will break down and stop working.
What is the wholesale price?
As the wholesalers do not send the products directly to the customers, so the wholesale price differs from the one in the retail shops. They are a linking side between the manufacturers and retailers. Wholesale price is the cost charged by the manufacturer or business owner from the retailer. Usually, the wholesale price is the lowest possible price for the bulk of items.
What is the retail price?
The retail price is the last price that appears on the labels in the stores or online store pages display on online store pages. It is the price that is set by the retailer for the end consumer. Retail price, as a rule, involves a significant markup.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Retailers
Summing up the previous thoughts on the definitions of wholesale and retail selling strategies, retailers are often referred to as “the linkage between suppliers, i.e., wholesalers and consumers.” The retailers’ role is significant, as they need to decide the final price of products sold in stores. In fact, retailers often appear to be under pressure to raise or reduce costs. For instance, they usually must pay their way through operating margins, which may be as low as 5% or less than the wholesale price from suppliers for products being sold at the retail level. As a result, it’s not surprising then that many retailers choose not only to sell one product but rather multiple ones. Such a strategy is also known as product bundling.
Now that we have a clearer understanding of main retail pricing strategies let’s quickly surf through the pros and cons of becoming a retailer.
Main Benefits
Low Capital Requirements
Retailers don’t need to invest heavily in the capital. As a result, it has become an affordable option for anyone with a low budget. Thus, starting up a shop can be done without much hassle or debt risk!
Being an entrepreneur on the retail ground means you won’t have any upfront costs like setting up your store, getting inventory, or paying rent. All these things are taken care of by the manufacturers. The retailers make their profits by marking up the wholesale prices and selling them to the customers.
Credit Facilities
The benefits for retailers are many and varied, but one of the most important is that they can sell their products on credit.
This is a facility that wholesale businesses do not have, as they deal in much larger volumes and are not interested in taking the risk on smaller quantities. With such privileges, retailers can take time to pay for their stock, safe in the knowledge that they will not be penalized for late payments.
Main Drawbacks
Marketing Costs
Marketing is the backbone of any successful business, but it’s not always easy for small companies or new entrepreneurs to invest. This can be incredibly challenging when a retailer is just starting with their startup. In fact, allocating the budget towards marketing could mean missing out on other necessary expenses such as payroll!
Higher Competition
The market is overloaded with lots of products and sellers from various niches. Many other companies are vying for attention and dollars with their products (and prices). Thus, retailers often find themselves in a ruthless situation, where they have to be highly competitive, offer amazing deals and discounts to lure in buyers.
This is not the case with wholesale businesses. They can afford to sell their products at a slightly higher price because of the volume they are moving.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Wholesalers
Summing up the definition of wholesaling, let’s note that this system refers to businesses that sell goods or products in large quantities. A wholesaler typically buys large amounts of a product from a manufacturer or distributor and then sells relatively smaller quantities to retailers, who, in turn, sell the products to consumers.
Wholesalers have several advantages and disadvantages as compared to retailers.
Main Benefits
Discounts and Allowance
Wholesalers buy products in bulk from the manufacturers. Thus, one of the perks of becoming a wholesaler is receiving discounts, gifts, and special offers. As a result, the manufacturer or supplier may offer other discounts, allowances, and incentives to the wholesale buyer that are not available to the general public. The wholesale buyers may also receive extended credit terms from the supplier, which allows the buyer to purchase products over extended periods.
Lower Competition
Since wholesale buyers purchase in large quantities, there is usually less competition for buying products. This can give the buyer more bargaining power when negotiating prices with suppliers.
Main Drawbacks
Huge Capital Requirements
Wholesalers are faced with the challenge of investing large amounts of capital in purchasing goods in bulk. This can be a barrier to entry for new businesses. However, it is essential to keep in mind that going to extremes cannot be an option. Wholesalers need to preserve adequate stock levels to avoid overstocking or backordering.
Shipping and Storage Costs
Becoming a wholesaler means investing in a warehouse, inventory management software, and other strategic features. Wholesalers also have to bear the cost of shipping and storing their products. Additional expenses can add significantly to the cost of launching a new business.
Retail and Wholesale Price Difference
Wholesale businesses have some advantages. There is no need to advertise goods, rent a store or think about how to exhibit your interests. You only have to manage to deal with large amounts of items and communicating to the retailers. You as a wholesaler should also be ready to send out products to other countries and towns.
As for the prices, the wholesale price is always lower than the retail price. The retailer pays the product cost and the profit cost that the wholesaler has set.
The owners of shops (no matter brick-and-mortar or online) buy goods from wholesalers having an aim of selling them to their customers. On their turn, they can also trade both in retail or wholesale. Retail price is higher than the wholesale. The retailers set the prices themselves. In contrast to wholesale, they do not vary depending on the number of items. But it can be lowered from time to time if the seller decides, for example, to announce a discount.
As for the higher price in retail, it comprises the costs. In the retail business model, there are costs of advertisements, packaging, salaries, bills, on e-commerce the paid plans for the platforms used and many more. A retailer should take into account every single detail essential for the customer experience.
Retail price formula and wholesale price formula
How to calculate the retail price
There exist different strategies for different types of businesses; they should be taken into account when setting up retail prices. It would be best if you started researching the market and holding a price comparison. And also the client segment should be of great importance: you’d better know whom to you sell.
Before coming straight to the point of setting a price, you should find out the wholesale price. Then you should add the profit margin that usually is aimed to be 55-65%. Of course, calculating the retail price is individual, it depends on your business type, market, plans and more. One famous pricing strategy that is called SRP (Suggested Retail Price), calculates the retail price according to the formula:
Retail Price Formula: Retail Price = Wholesale Price / (1 – Markup Percentage)
How to calculate wholesale price
Not only wholesalers need to find out the wholesale price. Retailers need it as well to calculate the retail price. For a wholesale price calculation, you need to know the COGM (cost of manufactured garments). It includes the fee required to make the product, as well as the materials, shipping, handling, labour and others spent on the final product.
Cost of Goods Manufactured Formula
COGM = Material Cost + Labor Cost + Additional Costs and Overhead
Wholesale Price Formula
Wholesale Price = Materials Cost + (Labour Invested x How Much You Value Time) + Other Overheads (Rent, Fixed Costs, Electricity, etc.) + Profit Margin
Defining Value-Based Pricing
Before passing on the main steps, let’s define value-based pricing strategies.
In a nutshell, value-based pricing is setting a price for your product or service based on the value it provides to the customer. In contrast to cost-based pricing, which forms the prices based on how much it costs to produce or deliver the product or service, value-based pricing considers the needs, preferences, and spending power of the consumers.
There are a few key reasons why value-based pricing can be a smart move for businesses.
- Firstly, it can help you stand out from your competition. If all of your competitors are charging based on cost, you can set yourself apart by charging based on the value your product or service provides. When potential buyers know that they’re getting a good deal for their money, they’re more likely to choose you over hundreds of your competitors.
- Secondly, value-based pricing is a working tool for both retailers and wholesalers.
- Thirdly, it can help entrepreneurs increase their profits. By pricing a product or service based on its value to the customer, business owners can ensure that they are making a good return on investment for each sale.
Of course, implementing a value-based pricing strategy takes some effort. You need to accurately assess your product or service’s value to the customer and communicate that value clearly and concisely. But if business owners can get it right, value-based pricing has the potential to become a powerful tool for success.

Steps for Using Value-Based Pricing
#1 Analyze the market to get insights into the customer’s basic needs and expectations.
#2 Don’t underestimate your competitors. Studying the prices can help you understand the essence of their pricing strategies and develop yours accordingly.
#3 Assess the value of your product or services. Does it correspond to the golden mean established on the market?
#4 Test and review the prices to see whether your strategy is the best fit for your target audience.
Closing Points
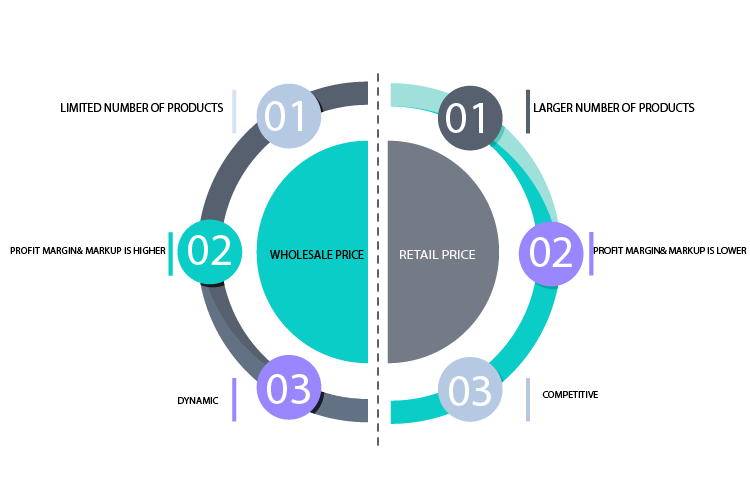
If summarizing the topic, we can mention the key differences between Wholesale and Retail according to several points:
- Products in wholesale are more limited, while in retail, the number of products to work with is larger.
- Profit margin and markup is higher in retail than in wholesale.
- You can reach a broader range of customers through wholesale selling your items in different stores. In retail, you usually trade in just one particular store.
- Retail business is more competitive than wholesale.
No matter what type of business you choose – retail or wholesale, in the supply chain process, there is one crucial step – inventory management. Both retail and wholesale should have specific approaches to management. It is suitable for any business holder to think about the budget supposed to spend on inventory management when setting prices (both wholesale price and retail price). When considering and planning your costs as a retailer or wholesaler, you can use accounting software and calculators. eSwap tools can be of great importance for both. We have integrations with two of the leading and best accounting platforms (Xero and Quickbooks). As for the calculators, various free calculators (for example, eBay final value fee calculator or Amazon fee and profit calculator) are available. You can plan your business better and more effectively with the help of eSwap.







